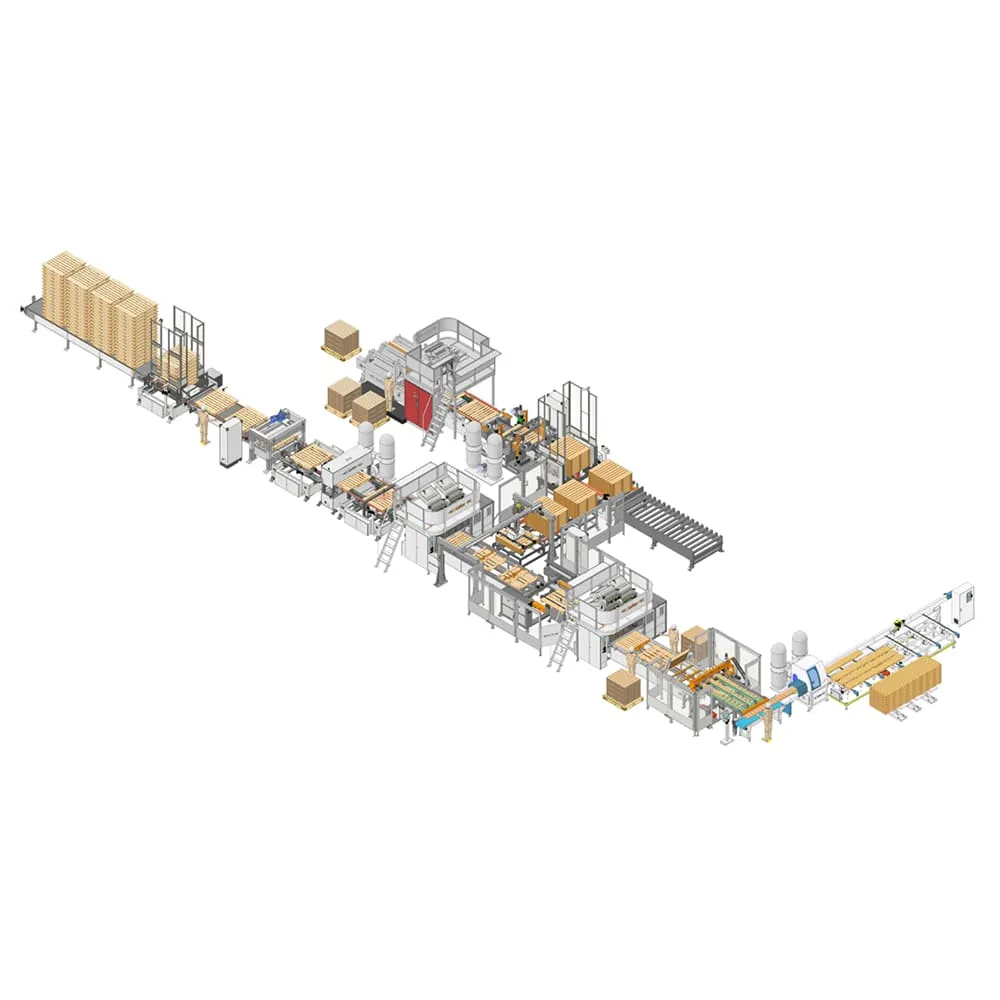
Pallet Nailing Machine Adaptation Process for Diverse Pallet Types
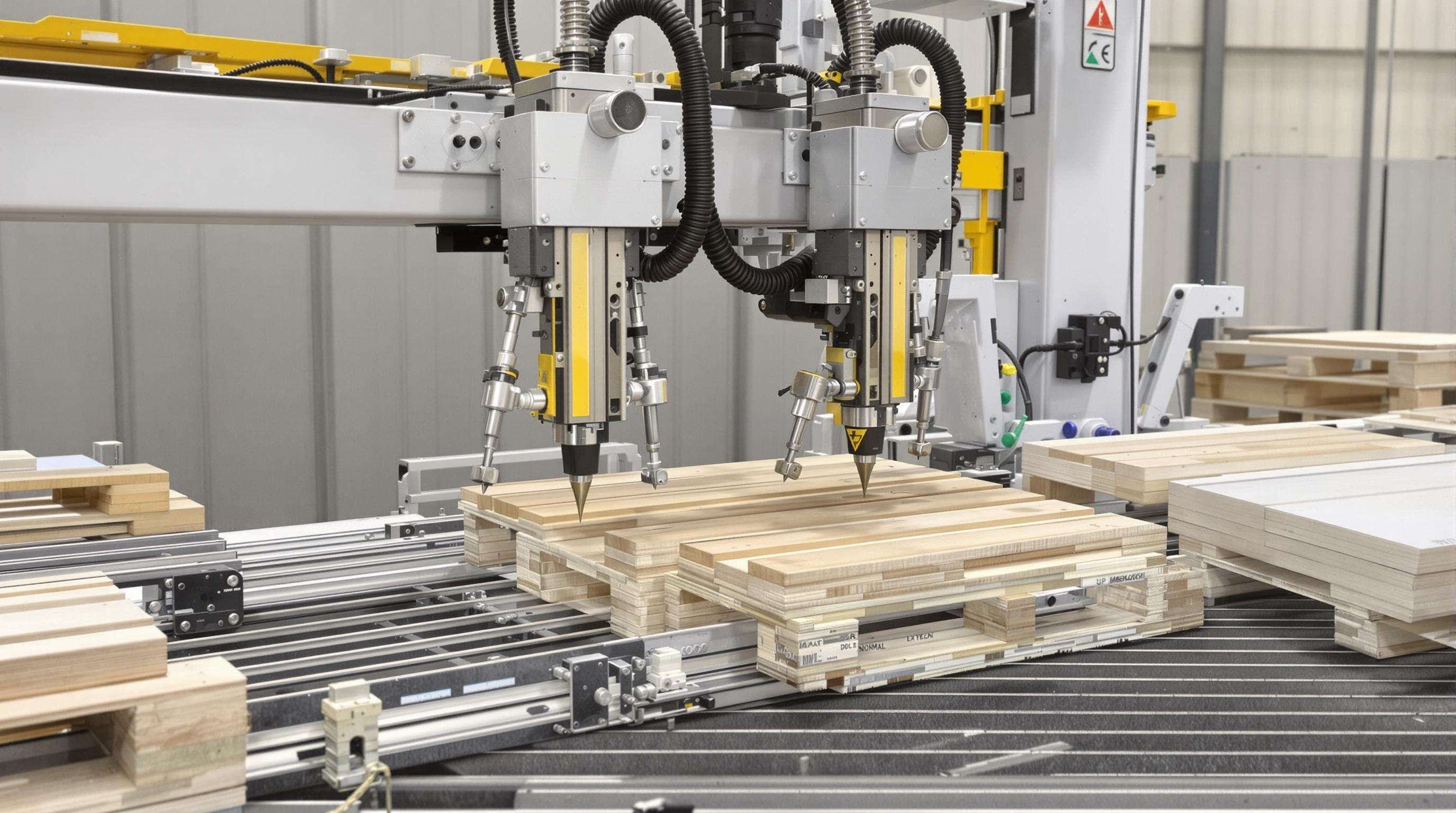

Modern pallet nailing machines achieve structural compliance across pallet types through intelligent parameter adjustments aligned with ISO 6780 standards for load testing. This adaptation process addresses four critical technical considerations for optimal performance.
Key Variables in Block Pallet vs. Stringer Pallet Configurations
Block pallets require 23% tighter nail spacing (1.8" vs. 2.3") compared to stringer designs to support mid-span load distribution. Critical configuration variables include:
- Fastener angle (90° vertical vs. 45° angled entry)
- Deck board alignment (perpendicular vs. parallel to stringers)
- Support point density (9-12 blocks vs. 3-5 beams per pallet)
Pressure Calibration for Composite vs. Wooden Materials
Composite pallet production demands 18-22 PSI lower hydraulic pressure than wood nailing to prevent material delamination. Softwoods like pine tolerate 5% pressure variation, while engineered boards require ±1 PSI precision to maintain layer integrity. Real-time pressure sensors automatically compensate for material density fluctuations during operation.
Nail Pattern Customization for Load-Bearing Requirements
Pallets rated for 2,000kg+ loads employ spiral nail patterns with 12-15 fasteners per joint, compared to 6-8 nails in standard configurations. Angled nailing (30°-45°) improves shear strength by 40% in heavy-duty applications through interlocking grain structures.
Quick-Change Tooling Systems for Multi-Format Production
Modular tool heads enable switchovers between pallet types in under 90 seconds through:
- Standardized mounting interfaces with magnetic alignment
- Pre-set depth gauges for material thickness variations
- RFID-tagged components that auto-configure machine settings
Core Principles of Pallet Nailing Machine Customization
Modern pallet nailing machines achieve versatility through three foundational engineering principles: modular design architectures, intelligent force modulation, and automated material compensation systems.
Modular Component Architecture for Custom Pallet Design
Interchangeable tooling systems form the backbone of adaptable pallet production. Standardized ISO 6780-compliant modules enable rapid reconfiguration between EUR-pallet, block-pallet, and stringer-pallet formats. Key exchangeable components include:
- Nail magazine assemblies with adjustable feed rates
- Multi-axis positioning guides for alternate deckboard patterns
- Rotational head units accommodating 90° or 180° fastening angles
Dynamic Force Adjustment Algorithms
Advanced servo-pneumatic systems automatically regulate impact forces from 2.5 kN to 12 kN based on material density readings. Real-time sensors measure workpiece hardness during the feed cycle to:
- Prevent wood splitting in low-density pine ( ≤ 480 kg/m³)
- Ensure full nail penetration in hardwood applications ( ≥ 720 kg/m³)
- Maintain consistent fastener seating in mixed-material pallets
Material Thickness Compensation Mechanisms
Laser-guided thickness profilers eliminate manual shim adjustments through automatic Z-axis repositioning. This technology accommodates:
| Material Variation | Compensation Range | Tolerance Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Wood warping | ±6 mm | <1 mm deviation |
| Composite stacking | ±11 mm | <2 mm deviation |
| Moisture expansion | ±3.5 mm | <0.5 mm deviation |
Industry Case Studies: Pallet Nailing Machines in Action
Automated EUR-Pallet Production Line Optimization
Modern pallet nailing machines achieve 30% faster cycle times in EUR-pallet production through automated deckboard alignment systems. These systems automatically adjust for the EUR-pallet's signature 1450×1200 mm dimensions and 78 kg load capacity requirements. Implementation of dynamic pressure sequencing algorithms enabled one facility to handle 800 pallets/shift without manual retooling.
Chemical-Resistant Pallet Manufacturing Solutions
For chemical-load applications, pallet nailing machines integrate corrosion-resistant tooling that withstands pH levels from 2.5–12.7. Advanced moisture sensors prevent material degradation by maintaining optimal 9–12% wood moisture content during assembly, critical for pharmaceutical and agricultural logistics.
Integrating Automation into Pallet Nailing Machine Workflows
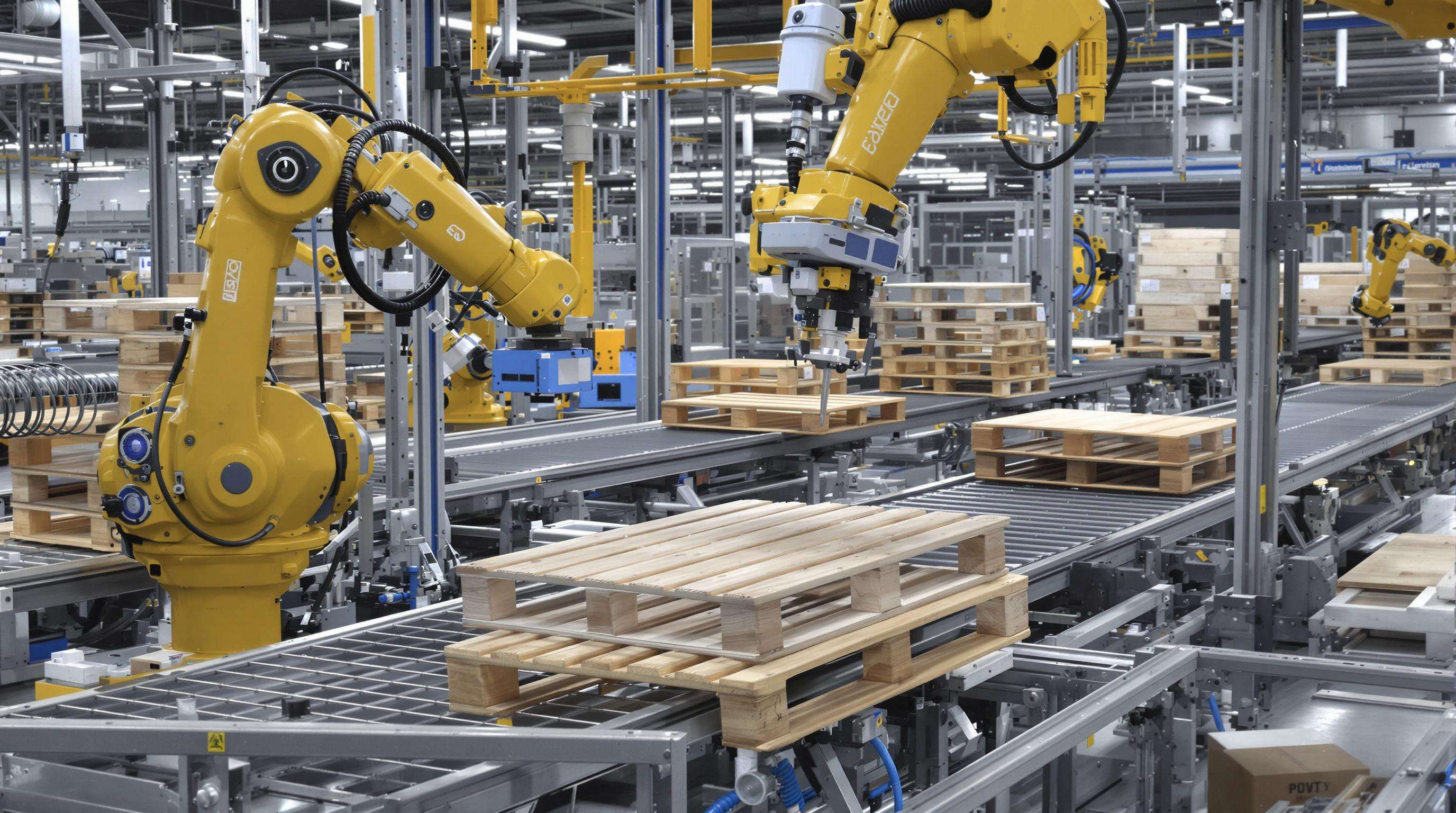
Robotic Pallet Positioning Systems
Modern robotic pallet positioning systems utilize servo-controlled manipulators that align wooden components within ±0.5mm tolerance. This automation eliminates manual measurement errors while achieving positioning speeds exceeding 120 components/minute.
Machine Vision for Defect Detection
Vision-guided defect detection systems employ high-resolution CMOS sensors paired with AI classifiers to inspect 15+ quality parameters simultaneously. These systems analyze board alignment accuracy, nail penetration depth (maintaining 28-32mm specifications), and structural integrity at production line speeds.
Emerging Trends in Pallet Nailing Machine Technology
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Systems
AI-driven predictive maintenance systems analyze real-time sensor data from vibration patterns, motor currents, and pneumatic pressures. Machine learning algorithms process historical performance data to forecast maintenance needs for critical parts like nail drivers and air compressors.
FAQ
What are the key differences between block and stringer pallets in terms of nailing?
Block pallets require tighter nail spacing to support mid-span load distribution, while stringer pallets need longer spacing. The fastener angle and support point density also vary between the two pallet types.
How do pallet nailing machines handle different materials?
Pallet nailing machines adjust hydraulic pressure levels and employ real-time pressure sensors to accommodate material density fluctuations. This ensures that both wooden and composite materials are nailed effectively.
What role do AI-driven systems play in pallet nailing machines?
AI-driven systems are crucial for predictive maintenance. They analyze sensor data to forecast the maintenance needs of essential parts such as nail drivers and air compressors.